We'll be back in a bit !
The system is currently undergoing a routine upgrade to ensure you get the best learning experience. The maintenance is expected to continue till 8:00 pm. Please check back later.
Thank you for your understanding!
While we know that thermodynamic variables such as pressure, volume, and temperature affect the expansion and compression of gases, properties like the internal energy, enthalpy, and entropy also play a role. Enthalpy and energy are related concepts and in an ideal gas, the internal energy and enthalpy depend solely on temperature of the system. In fact, enthalpy changes at constant pressure involve heat supplied by or to the system, and the change in enthalpy for a reaction equals the heat absorbed or released. In accordance with the law of conservation of energy, heat flows from hotter body to colder body. Enthalpy has the same unit as energy and depending on its sign, we can infer whether a process will or will not take place.
Heat transfer and temperature balance.
Enthalpy is a physical quantity in thermodynamics that is mathematically equal to the sum of the internal energy of the system and the product of pressure and volume.
From the above equation, we can also calculate the change in enthalpy at constant pressure or volume. Any change in enthalpy will be equal to the sum of the changes in the quantities on the right-hand side of the above equation.
In thermodynamics, enthalpy is generally denoted by the letter H and is related to the heat content in a system. Its unit is the same as energy and thus, it is also measured in Joules.
Enthalpy and heat
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with quantities like pressure, temperature, volume, and their relation with internal energy, heat, and work. It is governed by three universal laws that can be stated as follows:
Let dQ be the amount of heat exchanged by the system, dU be the change in internal energy, and dW be the work done on or by the system. The first law then formulates the law of conservation of energy and states that the heat exchange equals the sum of the change in internal energy and work done. That is,
The second law forbids an engine that is 100% efficient. It has various statements, but the simplest one says that it is impossible to design an engine that converts all heat input into work. According to this law:
Another statement of this law is the Clausius Statement, which says that no machine exists that can transfer heat from a body of lower temperature to one of higher temperature without external input.
If systems A and B are in equilibrium, and B is in equilibrium with C, then A and C are also in equilibrium with each other.
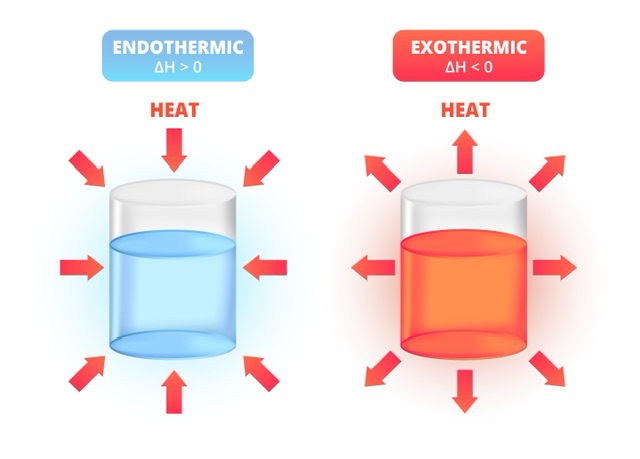
Enthalpy is a crucial factor in determining the amount of heat energy in a system and it also helps us infer whether a chemical reaction is endothermic or exothermic. It represents the heat content of a system at constant pressure and is related to the energy lost or gained by the system during a reaction. The concepts of enthalpy play a vital role in various aspects of our lives. For instance, engines and refrigerators can be studied on the basis of enthalpy. Further, various chemical processes are forbidden and using enthalpy, we can infer which one, aiding us in understanding chemical reactions.
When any chemical reaction occurs, it is accompanied by a change in total enthalpy of the system. This change can be estimated using the following formula:
Depending on whether this change is positive or negative, we can infer whether the reaction is endothermic and exothermic.
1. How much extra heat energy is required for a balloon to remain at the same temperature if external pressure is constant at 3.2 atm and the change in its volume is 3 L.
We know that
The situation stated here involves no temperature change, which is an isothermal process. For isothermal the temperature of the system does not change and we can write
Hence, the balloon will require extra 9.6 J of heat energy.
Enthalpy is a quantity in thermodynamics that is related to the heat content and change of a system. It can be determined absolutely and instead, we measure the change in enthalpy that can give us an idea about the chemical reaction in question. Enthalpy of an ideal gas depends only on the temperature. The concepts of thermodynamics are governed by three laws that are universally valid.
1. What is the relationship between enthalpy and internal energy in a chemical reaction containing gaseous reactants and/or products.
The relationship can be derived by using the ideal gas relation. By rewriting pressure and volume in terms of temperature and number of moles, we get
H=U+ngRT
2. In a cylinder filled with air, if we attach a piston and suddenly compress it, what will happen?
Rapid compression leads to an adiabatic process. That is, heat energy will not be exchanged and instead, there will be temperature change. After some time passes, the gas will attain thermal equilibrium with the surroundings.
3. Is it possible to make a heat engine with 100% efficiency?
A heat engine that is 100% efficient is forbidden via the second law of thermodynamics and thus, it is impossible to make one.
4. What factors affect enthalpy
Enthalpy is related to heat and is affected by:
Temperature
Pressure
Concentration of reactants
Amount of reactant and product
State of reactants and products
5. Can a gas be liquified by only increasing pressure?
Not always. There is a critical point of temperature below which, it is possible to liquefy a gas by increasing pressure. But above the critical point, no matter how much we increase pressure, the gas will not liquefy.
